When it comes to AHA vs BHA in skincare, it is important to know what each acids is and how they work so that you can achieve that smooth skin texture and natural glow that you wish to have without makeup. Chemical exfoliants like AHAs and BHAs have been staples in the skincare routine. These powerful ingredients are super beneficial for many reasons, like acne, anti-aging, and the complexion of your skin to take the dullness away. However, understanding how to use them correctly is essential for getting the best results without irritation. Let’s delve into all about Alpha hydroxy acids and Beta hydroxy acids!
When you incorporate AHA or BHA into a skincare routine, there should be a noticeable difference. The results will not be by overnight, but the use of consistent chemical exfoliants is absolutely helpful for your skin’s health.
This post is all about AHA (alpha hydroxy acids) vs BHA (beta hydroxy acids), what they are, and their benefits for skincare.
What Are AHAs?
Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs) are water-soluble acids derived primarily from natural sources like fruits, milk, and sugar. The most common AHAs include:
- Glycolic Acid: Derived from sugarcane, it has the smallest molecular size among AHAs
- Lactic Acid: Found in milk and pickled vegetables
- Mandelic Acid: Extracted from bitter almonds
- Malic Acid: Found in apples and pears
- Citric Acid: Derived from citrus fruits
- Tartaric Acid: Found in grapes
What Are BHAs?
Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs) are oil-soluble acids. The most common BHA in skincare is:
- Salicylic Acid: Derived from willow bark extract
Another acid sometimes classified as a BHA is:
- Betaine Salicylate: A gentler alternative to salicylic acid found in beets.
Skin Penetration: How Deep Do They Go?
The effectiveness of these acids largely depends on their ability to penetrate the skin:
AHAs: As water-soluble compounds, AHAs work primarily on the skin’s surface. They can penetrate the upper layers of the epidermis but don’t go much deeper. This makes them excellent for surface-level concerns like texture and tone.
BHAs: Being oil-soluble, BHAs can penetrate much deeper than AHAs. They can work their way through sebum and into the pores, making them particularly effective for oily and acne-prone skin. This deeper penetration allows BHAs to address issues that originate below the skin’s surface.
However, since glycolic is the smallest molecule, it may go deeper than salicylic acid!
Related post; Hydrating skincare ideas
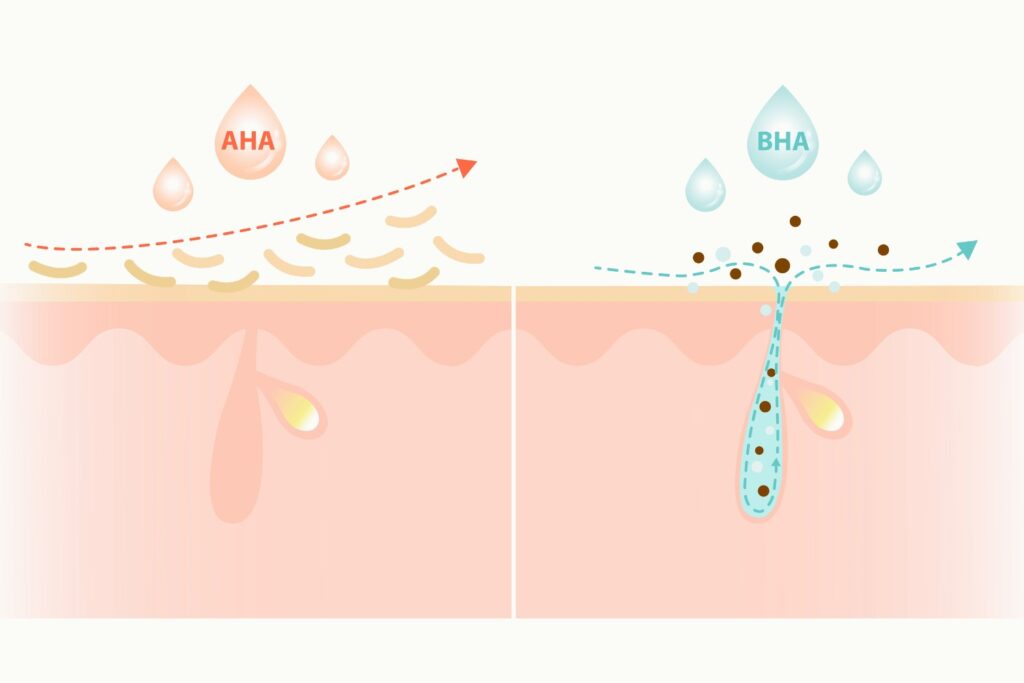
What Do AHAs Do for Your Skin?
AHAs work by dissolving the bonds between dead skin cells, effectively “ungluing” them from the surface of your skin. This exfoliating action reveals fresher, brighter skin underneath. Specific benefits include:
- Improving skin texture and reducing the appearance of fine lines
- Enhancing skin brightness and reducing hyperpigmentation
- Boosting moisture levels in the skin (especially lactic acid)
- Stimulating collagen production for firmer, more youthful skin
- Evening out skin tone and reducing sun damage
What Do BHAs Do for Your Skin?
BHAs go beyond surface exfoliation to provide:
- Deep pore cleansing, removing excess sebum and preventing clogged pores
- Anti-inflammatory properties that calm redness and irritation
- Acne-fighting abilities, targeting both existing breakouts and preventing new ones
- Gentle exfoliation that’s typically less irritating than AHAs
- Reduction in blackheads and whiteheads
Which Skin Types Benefit from AHAs?
AHAs are particularly beneficial for:
- Dry skin: They help remove dead skin cells that can make dryness look worse while also improving hydration
- Sun-damaged skin: They can help fade hyperpigmentation and improve overall texture
- Aging skin: They stimulate collagen production and reduce the appearance of fine lines
- Normal skin: They can help maintain a bright, even complexion
Which Skin Types Benefit from BHAs?
BHAs are ideal for:
- Oily skin: They help regulate sebum production and keep pores clear
- Acne-prone skin: Their anti-inflammatory properties help calm active breakouts
- Combination skin: They can target oiliness in the T-zone without overdrying other areas
- Sensitive skin: Especially in lower concentrations, BHAs have willow bark, which helps to be less irritating than AHAs
Concentration Ranges: Finding Your Sweet Spot
The effectiveness and potential irritation of both AHAs and BHAs depend largely on their concentration:
AHA Concentrations:
- Low (5-8%): Ideal for beginners or sensitive skin; provides gentle exfoliation
- Medium (8-15%): Good for regular use by most skin types
- High (15-30%): Professional or at-home peel strength; should be used infrequently
For specific AHAs:
- Glycolic Acid: Typically ranges from 5-30%
- Lactic Acid: Usually found in 5-12% concentrations
- Mandelic Acid: Commonly used at 2-10%
BHA Concentrations:
- Low (0.5-1%): Suitable for sensitive skin or daily use
- Medium (1.5-2%): Standard concentration for most products
- High (2-5%): Maximum concentration for over-the-counter products
Salicylic acid is most commonly found in concentrations between 0.5-2% in over-the-counter products.
Can You Use Both AHAs and BHAs?
Absolutely! Many skincare enthusiasts (or products) incorporate both acids into their routines, either:
- Alternating days: Using AHAs one day and BHAs the next
- Different times of day: For example, BHA in the morning and AHA at night
- Different areas: Applying BHA to oilier areas and AHA to drier areas
- Using products that combine both: Some formulations include both acid types in appropriate concentrations
Getting Started with AHAs and BHAs
If you’re new to chemical exfoliants, here are some tips:
- Start low and slow: Begin with lower concentrations and less frequent application
- Patch test: Always test new products on a small area first
- Sunscreen is non-negotiable: Both acids can increase sun sensitivity, so daily SPF is absolutely a must!
- Listen to your skin: If you notice excessive dryness or irritation, reduce frequency or concentration
Final Thoughts
Although sometimes it takes time to find out what works for your skin, chemical exfoliants are extremely helpful for your skin to improve skin’s health. Whether you’re dealing with stubborn acne, uneven texture, or signs of aging, AHAs and BHAs offer effective solutions for a wide range of skin concerns. By understanding the unique properties of each acid type and matching them to your specific skin needs, you can achieve remarkable results from your skincare routine.
Remember that consistency is key with chemical exfoliants, but so is moderation. These ingredients work best when they’re used appropriately as part of a balanced skincare regimen that also focuses on hydration, protection, and nourishment. And again, Never forget Sunscreen!
This post is all about AHA and BHA. What they are and how to incorporate them into a skincare routine.
Disclaimer: This blog provides general skincare advice and product recommendations. Always consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional.





Leave a Reply